Using Hybrid Cloud To Power Your Business
The concept of the digital “cloud” is what’s on everyone’s tongues as of late. Articles everywhere claim that cloud computing will be the future of human society. And, indeed, it certainly appears to be moving in that direction.
73 percent of businesses already rely on and run at least one application directly from the cloud. The reality is, the cloud isn’t just the future, it’s also already a very present reality. Companies that aren’t leveraging the cloud to better run their day-to-day business operations are at a distinct disadvantage to their competitors who are cloud-savvy.
However, while cloud computing is already here, many business owners still aren’t sure what the cloud is or how a hybrid cloud can help power their business into the future.
What Is The “Cloud” and “Cloud Computing”?
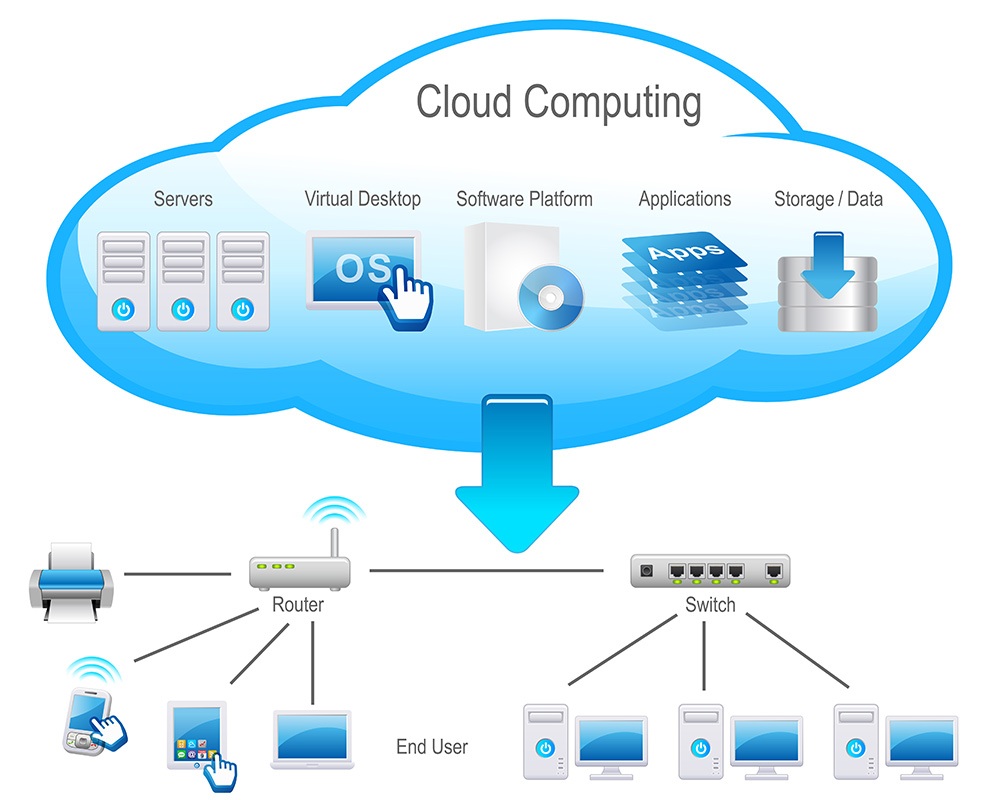
The “cloud” simply refers to the world-wide internet. The cloud is an invisible communication network through which services and communications can be delivered.
“Cloud computing” is computing done through the internet or the cloud.
Think of a personal work computer. When you use your personal computer, all processing power and storage (for the most part) happens on that computer. If you were to process some Word documents, for example, the personal computing device, whether it be a laptop, desktop, tablet, or smartphone, is performing all the necessary processing on the device itself. Furthermore, that Word file is generally stored onboard the device. If the device is slow, your experience will be slow. Likewise, if the device were to be destroyed or lost, you would also lose your files and documents stored on the device.
How The Cloud and Cloud Computing Work
The cloud and cloud computing works much differently. With the cloud, information is stored in a remote location, usually a data center. While you can manipulate the data on a local device with an internet connection, such as a personal computer, the file itself is physically stored in a different and often a secure location. That way even if the input device is lost or destroyed, your data remains safe “in the cloud.”

Likewise, cloud computing works in a similar way. Rather than supplying processing power via a local device, a computer located in a remote location, usually a data center, can do that processing for you via the internet.
The cloud is the result of the development and spread of broadband internet which allows for the transmission of enormous quantities of data anywhere in the world in an instant.
The information input in one location on the planet can instantaneously affect data elsewhere. Processing power in one place can be used to crunch data and perform work for customers on the other side of the world.
The outsourcing of digital storage and processing power to the cloud has transformed and will continue to transform the way we do business today and in the future. That is also why it is crucial for businesses to understand the different cloud computing models available to them today: private cloud, hybrid cloud, and public cloud.
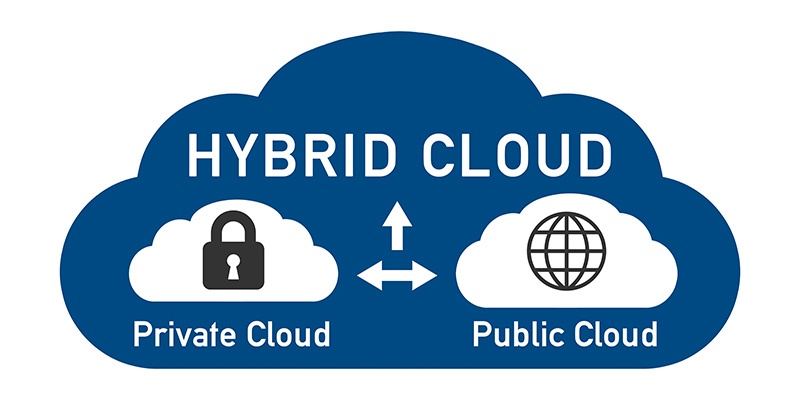
Hybrid Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud network that is wholly owned and controlled by one company, part, or entity. While processing power, digital storage, and cloud-based services are still pushed to company employees remotely, the data center from which the information is being pushed is located on-premises.
An excellent example of a private cloud in action is the corporate intranets and internal servers that many companies run. Information in the private cloud never leaves a company’s premises. While this can guarantee a higher degree of both control and security, private cloud infrastructure such as private data centers and servers are hugely and prohibitively expensive. Most small, medium and even very large companies have a limited capacity when it comes to running their own cloud infrastructure.
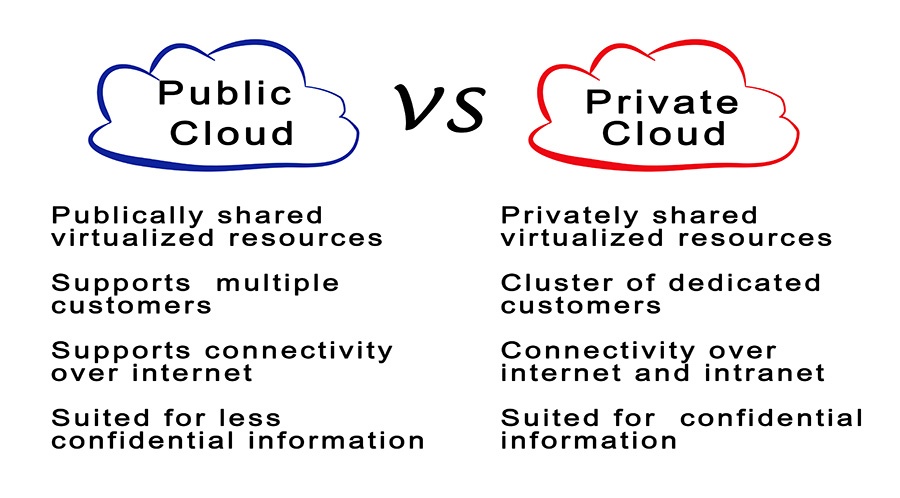
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a cloud network operated by a third-party provider (Such as Amazon, Google, or Microsoft). Computer processing resources, storage, and services are made available to the public via the internet. With a public cloud, all a company needs to set up and maintain cloud infrastructure is a good internet connection. Everything else is handled offsite by the provider. While the information stored on a public cloud is still proprietary, the data center itself is owned by someone else. The trade-off for using the public cloud route is a loss of control, less customization to individual needs, and crucially, less data security.
Both private and public cloud networks have significant advantages and disadvantages. In the not too distant past, companies needed to choose one or the other. Instead, businesses today can choose to implement a hybrid approach that incorporates the strengths of each cloud model while mitigating any potential drawbacks. The hybrid cloud approach is what many if not most Fortune 500 companies are already implementing.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
A hybrid cloud is a combination of both a private and public cloud approach.
A company or organization that implements a hybrid cloud utilizes a mix of both on-premises cloud infrastructure as well as cloud services provided by a third-party.
What makes a hybrid approach so successful is the orchestration between the two approaches. When executed well, a hybrid approach can leverage the strengths and synergies of both private and public clouds to meet a business’s core information technology needs.
An excellent example of a hybrid approach in action is a company that maintains their own localized data center and closed-circuit intranet to maintain sensitive data security while still utilizing third-party providers to handle mission-critical applications and associated IT infrastructure.
Another great example is a company that uses a private cloud service, such as VMWare — until it has met capacity at which point information is temporarily stored on a public cloud service. Once the company is able to expand its private cloud, the information is then migrated back onto their private network. This hybrid approach offers the flexibility and scalability of a public cloud approach while still maintaining some control and security offered by a private cloud strategy.
A hybrid cloud approach can power your business by leveraging the best that a private cloud and public cloud have to offer. A hybrid cloud strategy offers the best all-round security, customizability, operational flexibility, scalability, and cost-to-performance ratio.
Best All-Around Security
Customizable
Operationally Flexible
Superior Cost-To-Performance
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Cloud Products for Businesses
Data Backup and Recovery
Network Security
Learn more Learn more Learn more Learn more
Which Cloud Computing Deployment Model Is Best For You?
In most cases, a hybrid approach to the cloud is the best approach for the vast majority of companies in the marketplace. When implemented strategically and thoughtfully, a hybrid approach can give companies all the benefits of both a private and public cloud model with few, if any drawbacks.
However, the precise strategy and exact allocation of resources to a public or private approach will depend on the individual needs of each business. A business that requires maximum information security, for example, will be best served by a hybrid cloud strategy that leans heavily on private and on-premises infrastructure. A start-up with a limited IT budget and no in-house expertise might choose to outsource their cloud infrastructure to a third-party provider while still maintaining limited in-house private cloud infrastructure for crucial data. The various configurations and combinations of private versus public can be determined on a case-by-case basis.
Who Are Private Clouds Good For?
-
Government agencies
-
Security contractors
-
Companies dealing with sensitive information
-
Large corporations who need their own data centers to operate efficiently
Who Are Public Clouds Good For?
-
Individuals
-
Initial start-ups with limited IT resources
-
High growth companies that require maximum scalability
Who Are Hybrid Clouds Good For?
-
Almost everyone
-
Small, medium, large, and enterprise companies

