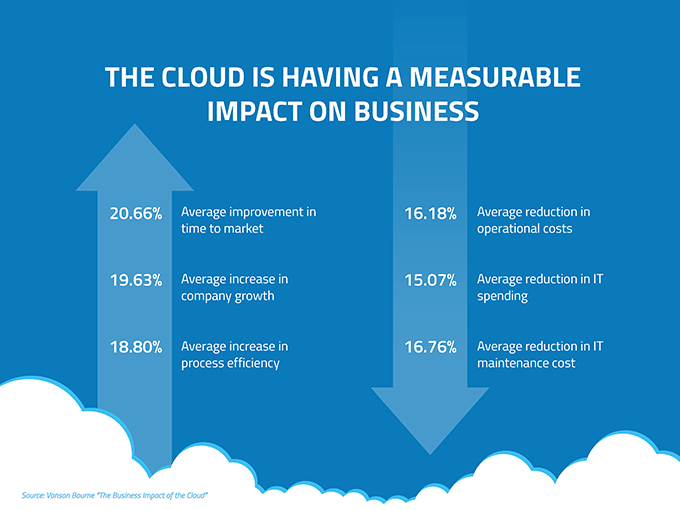
The cloud can change the way you do business.
Employee Mobility
Reduced Hardware Costs
Scalability for Future Growth
Running your business with cloud-based software and services is full of benefits extending beyond cost savings and reducing onsite hardware. The cloud can have a major impact on day-to-day operations.
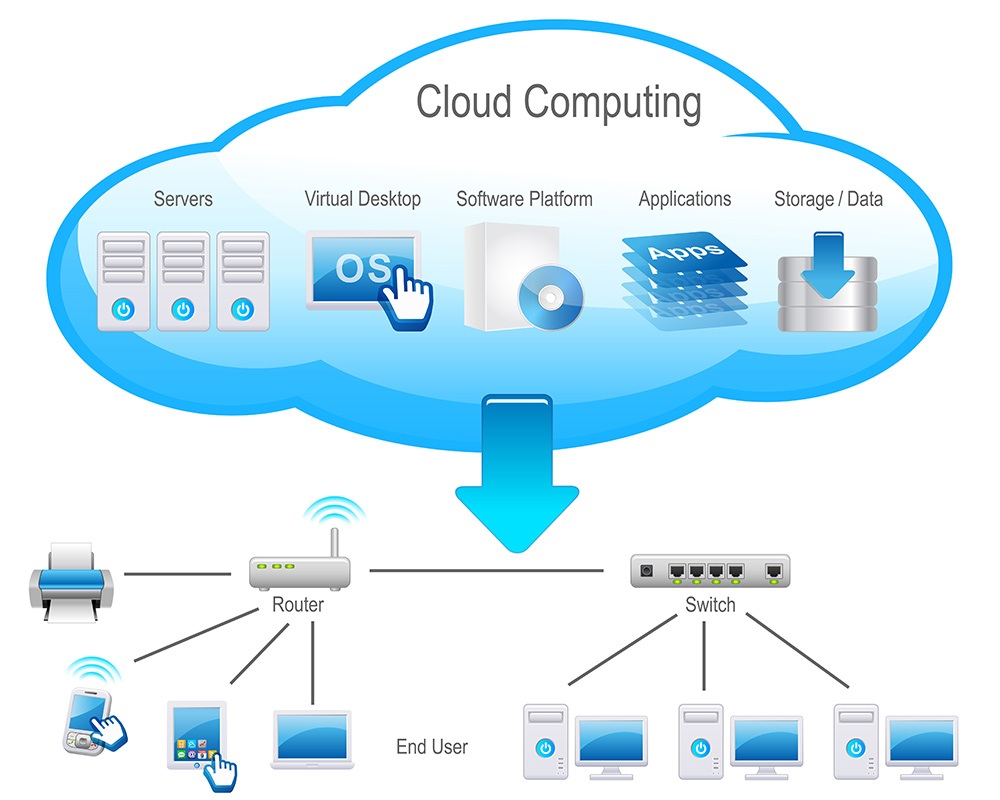
What Is The Cloud?

The cloud can change the way you do business.
Running your business with cloud-based software and services is full of benefits extending beyond cost savings and reducing onsite hardware. The cloud can have a major impact on day-to-day operations.
Employee Mobility

When your employees can be just as productive outside the office as they are inside your building walls, work where ever they physically are, it impacts how well and how much they can work. That equals greater productivity. Greater productivity equals greater profitability.
With the cloud, employees have to access work data and tools from anywhere with any device. Increased mobility has also been linked to advantages like greater employee engagement, sharper competitive edge, and overall better customer service.
In fact, 43 percent of employed Americans said they spent at least some time working remotely, according to a Gallop poll.*
Employees are pushing companies to break down the long-established structures and policies that traditionally have influenced their workdays.
Reduced Hardware Costs

Since parts of your infrastructure are virtualized and hosted offsite by your cloud provider, you don’t need as much computer hardware and other equipment – freeing up space in your office and the time costs maintenance and upgrades.
Scalability for Future Growth

With virtualized resources like cloud services, you can easily scale up or down with ease because this process is now the responsibility of your cloud provider. We tell your provider that you need more or less of something, and they deliver – sometimes within hours or even minutes.
Private vs Public Cloud
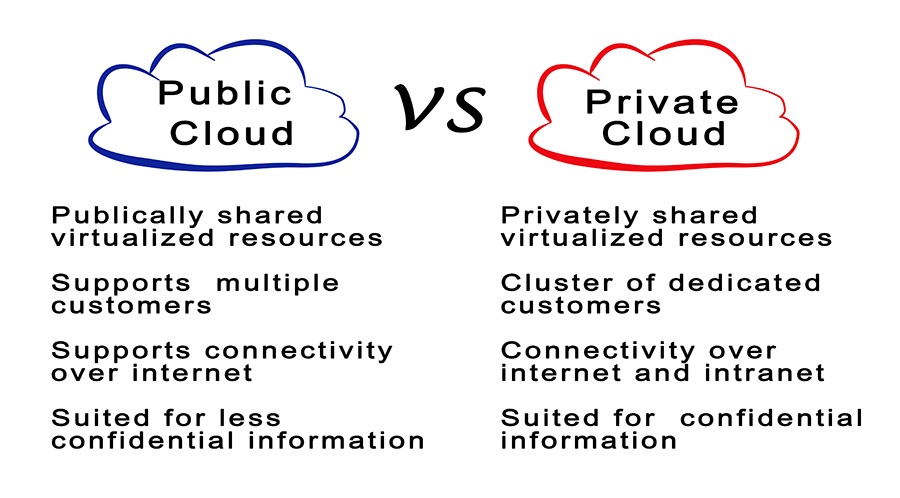
Not every cloud setup is created equal. Not only does each cloud provider have its own nuances, but there are also different types of cloud computing platforms.
Learn the differences between private and public clouds and the various options available in cloud computing.
Choose what’s most important, and that will dictate your cloud storage solution— public, private, or a hybrid.
Public Cloud – Ease of Use, Less Costly

A public cloud is usually less expensive to use, manage and maintain than a private cloud — which means most businesses operating in the cloud are operating in a public cloud. With a public cloud, your data is hosted inside a third-party data center. As a result, all of the maintenance, upgrades, and updates are handled by this third party.
The pay-as-you-go model allows a business to only pay for the resources you use, which can be appealing. And since all of the maintenance, updates, and upgrades are handled by the third-party vendor, you can also eliminate those types of ongoing costs.
Another major advantage of the public model is its relative simplicity, especially when considering the prospect of a business’s entire staff using various applications to perform their daily work. When adding BYOD mobile considerations and the capability to work from home, public service offerings make sense for many enterprises and some smaller and medium-sized firms. For many companies, usability and ease of use trump all other factors.
Although your data is still technically separated from other data in a public cloud, many organizations view it as insecure. So if your company is looking for more privacy and needs to meet industry standards like HIPAA or PCI, then a public cloud probably isn’t the right choice for you.
Private Cloud – More Privacy, Maximum Control
The private cloud works a little differently, mainly because the company itself hosts it. In other words, the data lives in the company’s data center — not with a third-party. Because of this, however, things can get a little more expensive.
All of the management and maintenance that goes with this private cloud is now the company’s responsibility; this includes the cost of these items. Nonetheless, this additional work and expense does involve a significant benefit.
A company has maximum control over its data with a private cloud and how it’s processed and stored. While access to important corporate data is obviously more secure in this scenario, it comes at the expense of usability and mobile access. In fact, a private solution is the only option in some highly regulated industries where data security is paramount. This means greater security — which goes a long way for a business that deals with very sensitive data or for one that needs to be HIPAA- or PCI-compliant. Also, none of a private cloud’s resources are shared. The dedicated data center manages only one company’s data.
However, at the end of the day, a private cloud still operates similarly to a public cloud. You can receive the same level of flexibility that a public cloud receives – it will simply come from an on-premise data center.
For some, a hybrid solution may be the best option: keep all-important corporate data secure behind some private cloud-based services stored securely using an array of on-premise servers with tightly controlled access. Read more.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
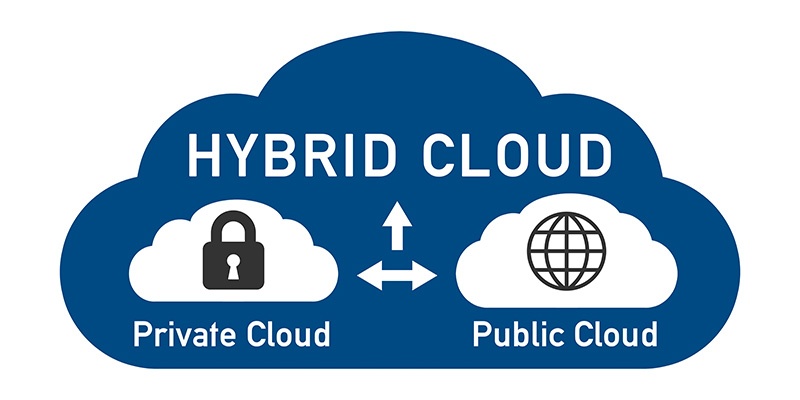
The best of both worlds.
The Hybrid Cloud: A mix of private and public cloud Services means mobile and web-based access to corporate applications with high usability, while important data remains secure.
If you are ready to take your data to the cloud, you’ll need to weigh the pros and cons of private vs public cloud storage solutions. One or the other could be incomplete which means you need a hybrid of both. It all boils down to the type of business you are running. Creating a hybrid cloud solution combining the advantages of both works quite well for a majority of today’s businesses.
Here are a few things to consider when choosing cloud services:
1. Privacy can be a challenge in the cloud.

Most businesses store at least some sensitive or proprietary data that could cause serious problems if it were hacked. Cloud providers often promise strict security, but data theft can still happen. That’s why it’s important to encrypt highly sensitive data before storing it in the cloud. Online tools such as Boxcryptor can be used to protect the confidentiality of your private information before it’s synced with the cloud, but these tools aren’t compatible with every cloud provider.
2. Your backups may need backups.

Many businesses turn to the cloud as a convenient option for backing up important files. It’s a good strategy: If something happens to a business’s local files, the data in the cloud remains untouched. But the inverse is also true. If a business stores all its important data in the cloud, it can be difficult to access it when outages and other failures occur.
In these cases, cloud providers make it a top priority to get their services up and running again quickly. That does little good for businesses that need to access their data immediately, however. When all of your data is stored in the cloud with no backups, you run the risk of losing that data forever. The best, most reliable way to avoid this problem is to back up all mission-critical data to
a local server.
3. There is fine print involved.

Many businesses turn to the cloud as a convenient option for backing up important files. It’s a good strategy: If something happens to a business’s local files, the data in the cloud remains untouched. But the inverse is also true. If a business stores all its important data in the cloud, it can be difficult to access it when outages and other failures occur.
In these cases, cloud providers make it a top priority to get their services up and running again quickly. That does little good for businesses that need to access their data immediately, however. When all of your data is stored in the cloud with no backups, you run the risk of losing that data forever. The best, most reliable way to avoid this problem is to back up all mission-critical data to
a local server.
Cloud Products for Business

Cloud-based applications have upended the way we used to do business and the multitude of ways in which we can interact with employees and customers.
Saving and accessing files on the Cloud is easy. The Cloud can also grow and change as your business needs grow and change. Most applications that use the Cloud automatically update themselves. These are all good reasons to take your business operations to the Cloud.
Following are a few common areas businesses typically migrate to the Cloud for.
Remote Working

New technology has given many business owners and employees the ability to leave their home or business offices behind and create mobile offices so they can work from anywhere, at any time. This kind of mobility eliminates geographic challenges and helps companies become nimble and more flexible.
We can help you create an operational mobile office that allows you and your employees to work from anywhere by sourcing the right mobile computer, getting reliable and secure internet connections, and making your data accessible.
Paperless

We can help you create a paperless office and digital document management system by scanning in hard copy files and creating a virtual file cabinet; managing finances, bookkeeping, and budgets on your computer; taking meeting notes on your computer, or transferring them later on, and using electronic agreements.
Once you create a digital document management system, you will have all of your paper documents accessible and searchable on your computer. And once those files sync to your online backup service, you can access them from anywhere, making your office truly mobile and paper-free.
Information Sharing

Whether you have in-house staff or a team in multiple locations spread across the country, the Cloud makes sharing data effortlessly. Once you have your data backed up to the Cloud, sharing files can be as easy as sending a link, eliminating the cumbersome process of emailing large files or saving copies on flash drives that are then mailed
File Storage & Data Back-Ups

The Cloud not only simplifies the process of backing up by allowing your data to automatically update as you work, but it also creates copies of your data off-site where it will be safe from any local natural disaster, theft, or malfunction.
Business Applications
Most of the most common business applications are now using Cloud-based services. Microsoft Office 365 probably tops all of them as a more universal and most versatile way to communicate and collaborate. Many others can track sales, manage projects, creative design, automate e-mail communication and sales follow-ups, manage and execute all accounting functions. Quite literally, there is a business application in the Cloud for nearly every task.
Phone Systems

You can use virtual phone lines and digital fax lines to create a telephone system you can bring with you wherever you go. This can help you run a professional and seamless business on the road or in multiple locations. The Cloud opens up a whole new world of low-cost unified communication capabilities, Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
Unified communication means integrating all means of communication into a single system. Features can include such as instant messaging (chat), presence information, voice calls and voice mail (telephony), mobility features (including extension mobility and single number reach), audio, web & video conferencing, desktop sharing, data sharing (including web-connected electronic interactive whiteboards), call control and speech recognition.
Real-Time Software Updates

Nothing reduces productivity more than booting up your computer, only to find that there is a slew of operating system and software updates that need to download and install. With could-based software, as soon as the program is open, it is already updated.
”Simply put, the Cloud makes things easier to control and quicker to implement — and at the end of the day, these are all things that promote efficiency.
Stephen Wright

